Elevators Algorithm(LOOK)
Elevators Algorithm
LOOK
Elevators algorithm is another disk scheduling algorithm, as the name suggest its roots lay in the working of an elevator. i.e, Once started it traverse in the same direction, being said that there are various modifications of an elevators algorithm and we will look at four of them.
In this post we will see LOOK algorithm, with complete cpp code of stimulation of LOOK algorithm.
Look is a simple algorithm which simply does a scan and until it reaches current end of the request at one end it keeps moving the head and if there are no more request pending ahead it changes its direction. When there are no request left, we will terminate.
Modifications:
- SCAN
- LOOK
LOOK
Look is a simple algorithm which uses concept similar to SCAN algorithm. In LOOK algorithm, we scan until we reach the last request at that end (NOTE: We do not proceed further until the tape ends) and then we turn our tape head to the other direction and do the same in that direction. When we reach a point where the request halts, we will terminate our stimulation for the reasons of making our stimulation simpler.
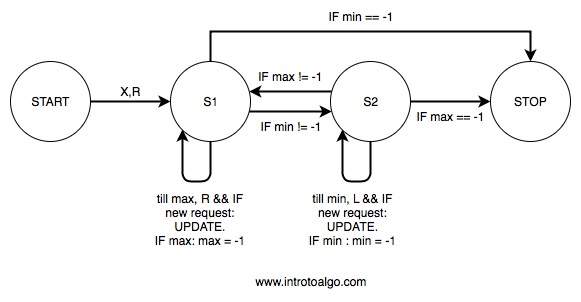
Note: In the above diagram, we are giving minimum priority for terminating the program. i.e. IF min!= -1 would be checked first rather than IF min == -1.
Suppose, We have head pointing at position X and we choose the direction to be right then the algorithm for LOOK would be given as follows:
- Till we reach Maximum request move Right and keep updating.(IF reached max := -1)
- IF minimum exists, change state to S2. Else STOP
- When at state S2, Till we reach minimum request, move Left and keep updating.(IF reached min := -1).
- IF maximum exists, change state to S1. Else STOP.
Simple Logic:
- Move towards max
- update if new request
- change direction
- move to min
- update if new request
- LOOP
CPP code for LOOK:
Written By, Sarvesh Bhatnagar
You may also like